Bruce S. McEwen1 and Peter J. Gianaros2
- Harold and Margaret Milliken Hatch Laboratory of Neuroendocrinology, The Rockefeller University, New York, New York 10065; email: mcewen@mail.rockefeller.edu
- Departments of Psychiatry and Psychology, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania 15213
Annu. Rev. Med. 2011. 62:431–45
Keywords
brain-body medicine, brain plasticity, hippocampus, amygdala, prefrontal cortex
Abstract
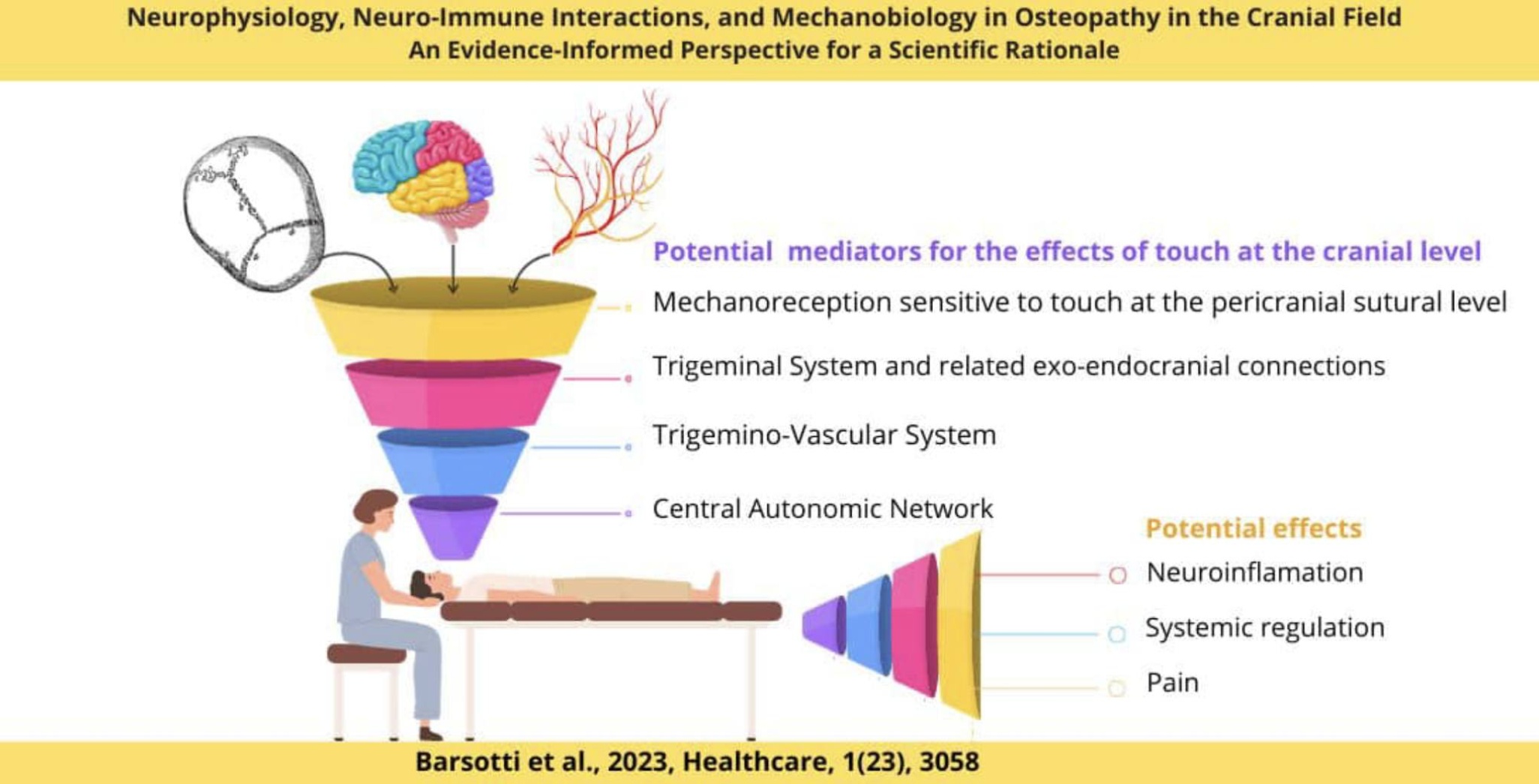
The brain is the key organ of stress processes. It determines what individuals will experience as stressful, it orchestrates how individuals will cope with stressful experiences, and it changes both functionally and structurally as a result of stressful experiences.Within the brain, a distributed, dynamic, and plastic neural circuitry coordinates, monitors, and calibrates behavioral and physiological stress response systems to meet the demands imposed by particular stressors. These allodynamic processes can be adaptive in the short term (allostasis) and maladaptive in the long term (allostatic load).Critically, these processes involve bidirectional signaling between the brain and body. Consequently, allostasis and allostatic load can jointly affect vulnerability to brain-dependent and stress-related mental and physical health conditions. This review focuses on the role of brain plasticity in adaptation to, and pathophysiology resulting from, stressful experiences. It also considers interventions to prevent and treat chronic and prevalent health conditions via allodynamic brain mechanisms.
Brain Behav Immun. 2011 Jan;25(1):25-39. Epub 2010 Sep 9.




















Devi effettuare l'accesso per postare un commento.